Liver Functioning
Chemotherapy Pump Helps People with Metastatic Liver Cancer Live Longer
It is implanted in your skin between your ribs and your pelvis and connected by a small catheter into the hepatic artery, which supplies blood to your liver. We usually implant the pump while we're performing surgery to remove liver tumors. Traditional chemotherapy is given by vein (or through IV), so it gets diluted through your whole body.

Hepatic Arterial Infusion Pump Offers New Hope to Patients with Liver
Hepatic artery infusion pump (HAIP) chemotherapy is an approach which allows direct infusion of chemotherapeutic into the liver and is especially useful in the setting of multifocal liver metastases. When combined with systemic chemotherapy, HAIP improves the response rate, provides more durable disease control, and in some patients leads to.
Chemotherapy Pump Helps People with Metastatic Liver Cancer Live Longer
HAI delivers chemotherapy directly to your cancer cells in the liver, limiting how much of the drug reaches healthy parts of your body. HAI allows doctors to flood the liver with a powerful dose of medication, as much as 400 times higher than standard chemotherapy. The liver breaks down 95% of the medication, greatly reducing side effects.

Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy for Colorectal Liver Metastases
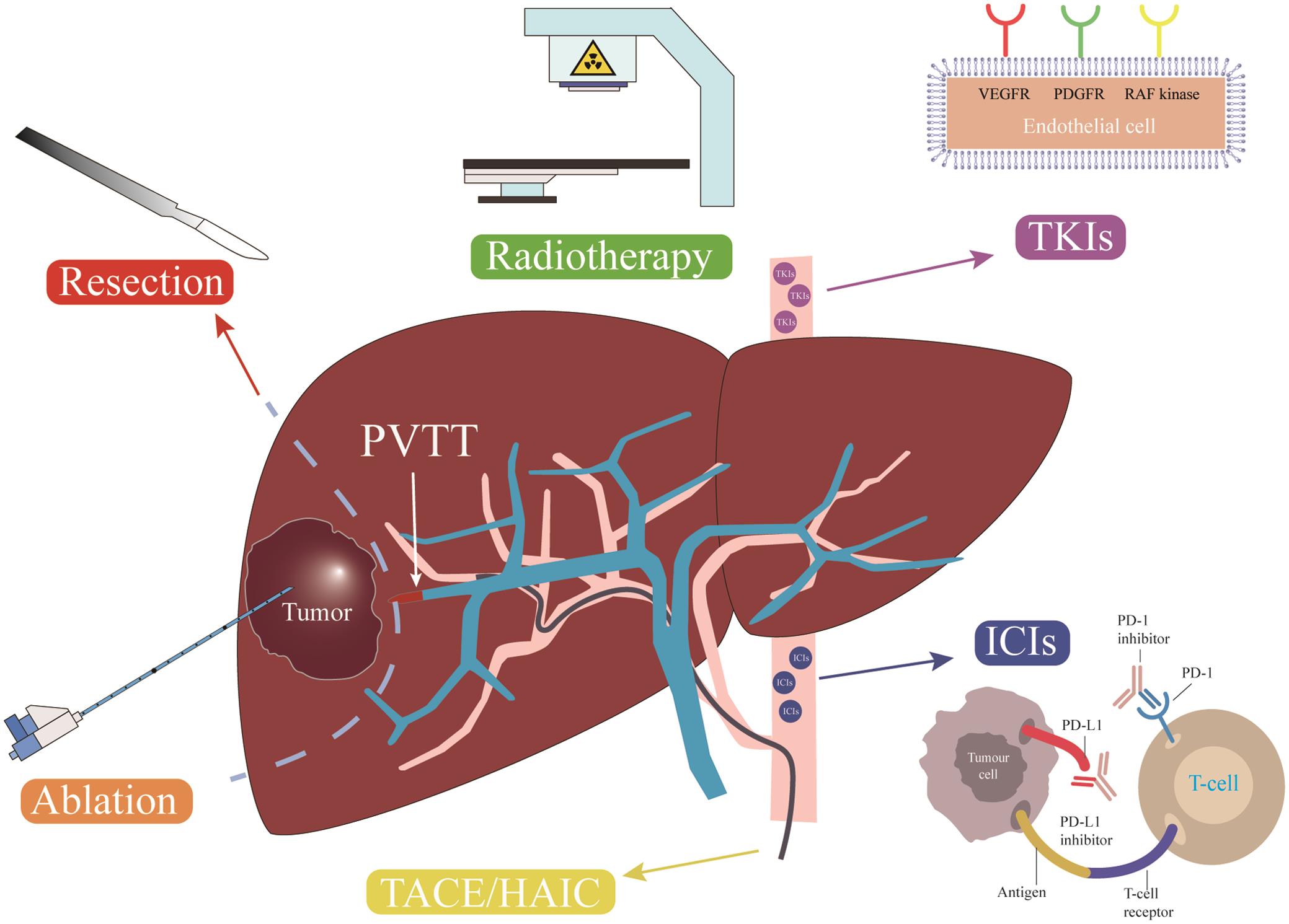
Hepatic arterial infusion (HAI) chemotherapy is the physiologic and pharmacologic isolation of the liver. 1,2 Primary and secondary liver tumors derive their blood supply from the hepatic artery, whereas non-tumor-bearing parenchyma receives dual blood supply from the artery and portal vein.
to JCTH
General side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and diarrhea, can be expected from any chemotherapy drug or combination of drugs, but side effects vary from patient to patient. Talk to your doctor about possible side effects before starting a chemotherapy treatment regimen. 800-826-4673. Request An Appointment.
(PDF) Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy Combined with Radiation
Hepatic arterial infusion (HAI) entails the surgical implantation of a subcutaneous pump to deliver chemotherapeutic agents directly to the liver in the setting of primary or secondary liver cancer. The purpose of HAI chemotherapy is to maximize hepatic drug concentrations while minimizing systemic toxicity, facilitating more effective treatment.

Current and Future Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma An Updated
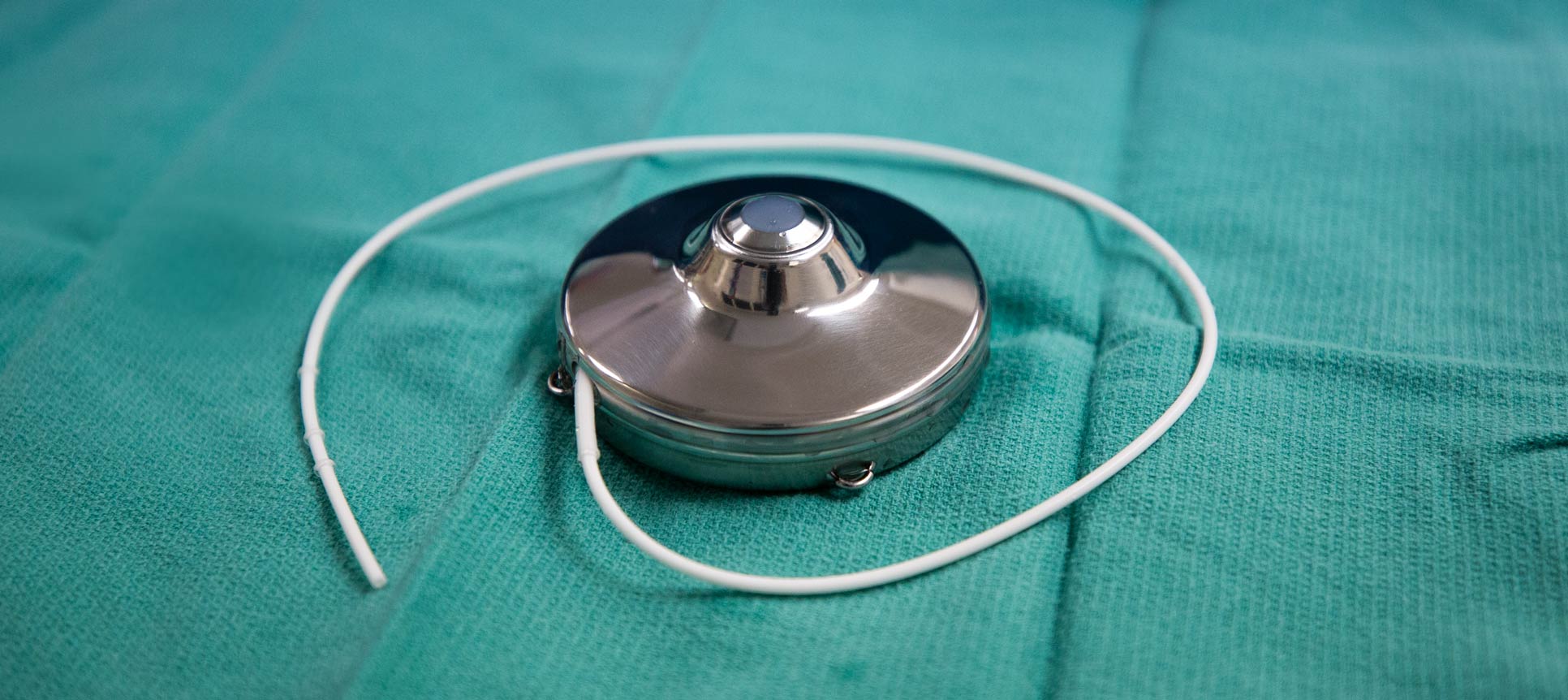
About Your Intera 3000 Pump. You will get your medication through a Intera 3000 hepatic artery pump. Your hepatic artery pump is a small, round device made of titanium metal. It's about 2 or 3 inches wide, about 1 inch thick, and weighs about 4 ounces. It's about the same size as a hockey puck. Your hepatic artery pump has 4 main parts (see.

Research Overview Hee Jeung Oh Research Lab
The liver-directed therapy involves surgically placing a pump directly into a branch of the hepatic artery. In some cases, the pump can be placed using robotic surgery. Chemotherapy is then delivered directly to the liver in a course of treatment that typically lasts six months, with visits to Mayo Clinic in Minnesota every two weeks.

Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy for Colorectal Liver Metastases
Hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) is a well-established and common treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), particularly in East Asia. However, HAIC is not recognized internationally.. Korean Liver Cancer Association 2018 Korean Liver Cancer Association-National Cancer Center Korea Practice Guidelines for the.
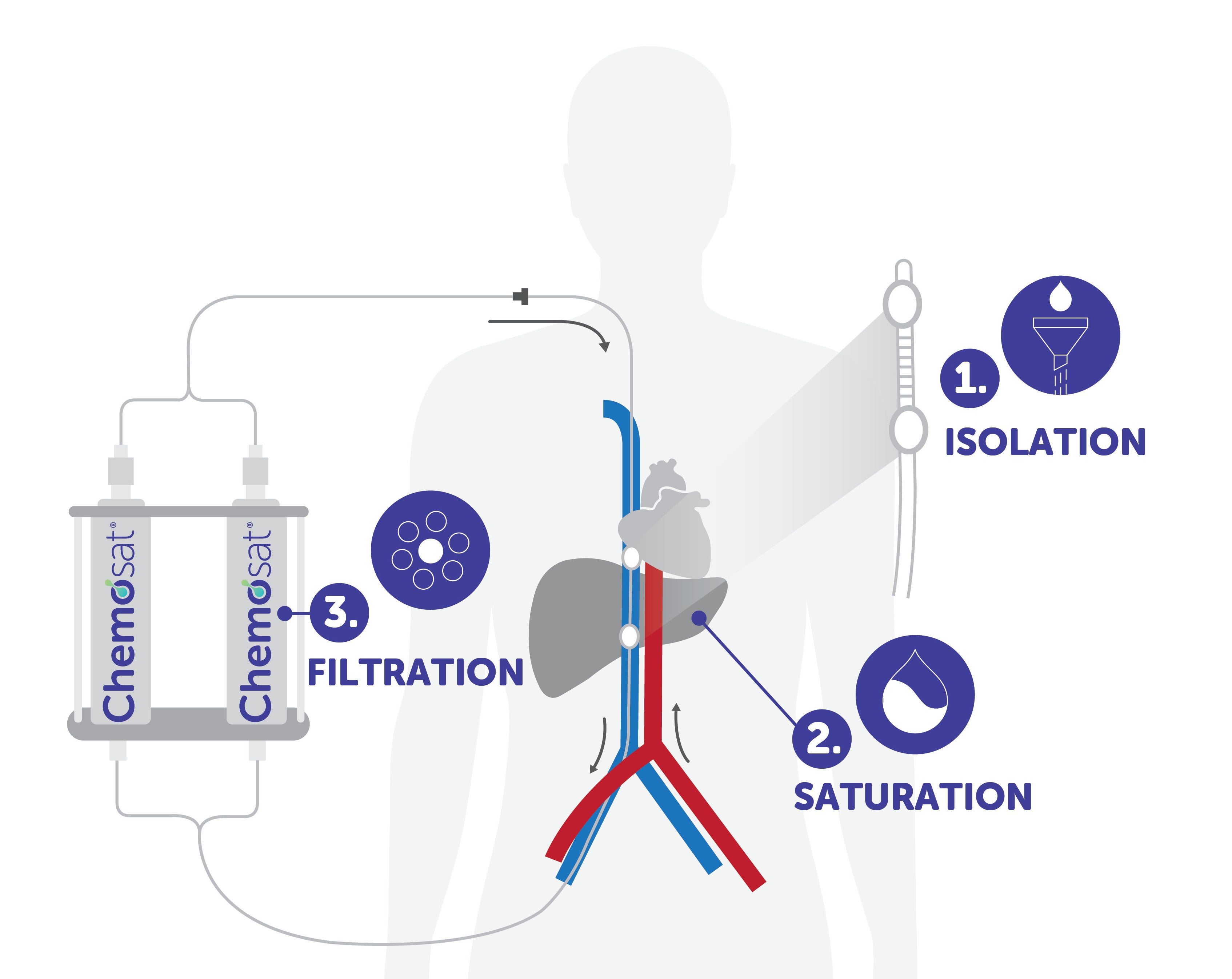
Chemosaturation Therapy A New Liver Cancer Treatment
Kemeny NE, Gonen M. Hepatic arterial infusion after liver resection. New England Journal of Medicine. 2005 Feb; 352(7): 734-5. Jarnagin WR, Schwartz LH, Gultekin DH, et al. Regional chemotherapy for unresectable primary liver cancer: results of a phase II clinical trial and assessment of DCE-MRI as a biomarker of survival.
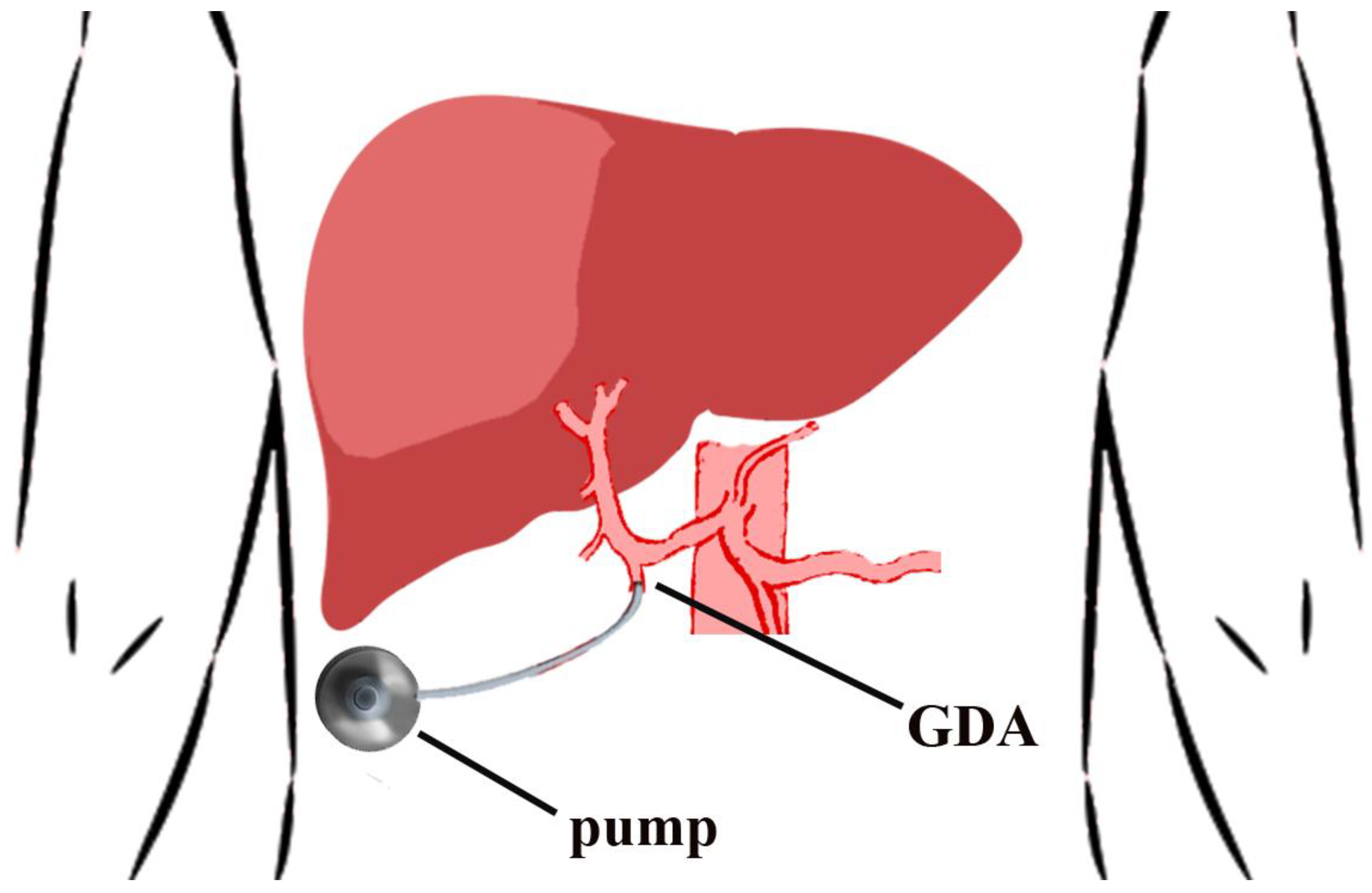
JCM Free FullText Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy for
Hepatic artery infusion, or chemo given directly into the hepatic artery, is regional chemotherapy that can be used for liver cancer. Hepatic artery infusion Doctors have studied putting chemo drugs directly into the hepatic artery at a constant rate to see if it might be more effective than systemic chemo.

Figure 2 from Mitomycinbased hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy
Hepatic arterial infusion delivers chemotherapy through a pump that's implanted in the abdominal wall. "We then use a catheter to deliver high doses of chemotherapy through the hepatic artery, which directly feeds metastatic tumors in the liver," said Peter Allen, MD, a Duke surgical oncologist. Even though the HAI pump delivers.

Hepatic artery infusion pump chemotherapy Surgical treatment for
1. Introduction. Liver functional failure is one of the most frequent and critical causes of cancer-related morbidity and death. Primary liver tumors grow up mainly in the liver, and thus happens for liver metastases deriving from other organs having a lower burden of disease at the primary site [1,2,3].Normal liver parenchyma is one of the most sprinkled body districts, having two distinct.
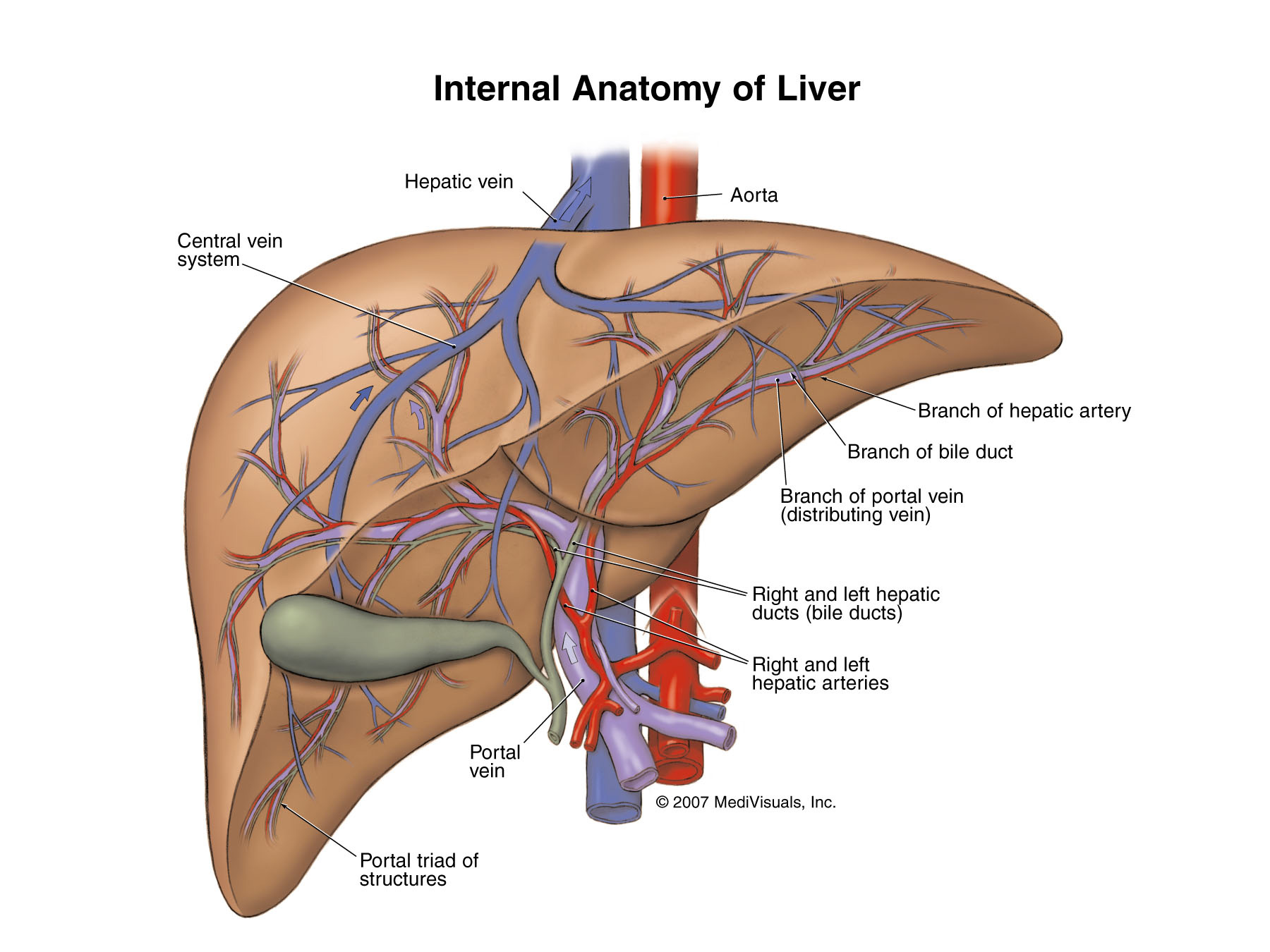
Liver Functioning
Hepatic Artery Infusion Chemotherapy: A Quality Framework. Despite well-established guidelines for screening and prevention, colorectal cancer remains highly prevalent in the USA with more than 150,000 new cases diagnosed annually. 1 Among this population, nearly 25% will develop liver metastases throughout their disease course and 50-75% of.
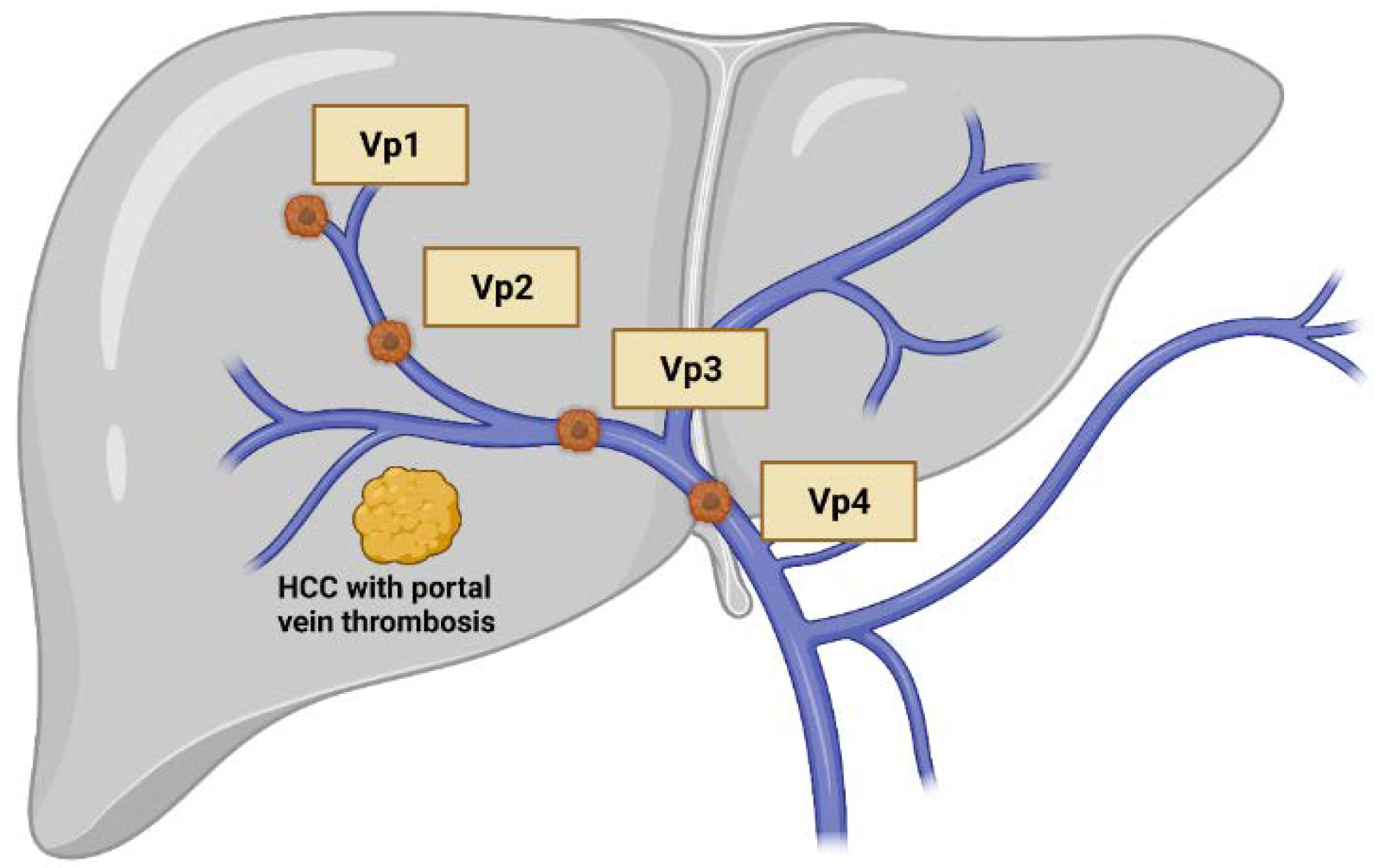
IJMS Free FullText Revisiting Hepatic Artery Infusion Chemotherapy
In the article that accompanies this editorial, Li et al 1 conducted a randomized controlled trial in patients with large hepatocellular carcinoma and found that hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy more often downstaged patients to resection and ultimately prolonged overall survival compared with those treated with chemoembolization. Although the results are encouraging, the technical.

(PDF) Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for liver metastases from
Objective: To compare the efficacy and safety of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for the treatment of high-risk hepatocellular carcinoma (hHCC) patients. Methods: Between January 2014 and August 2022, a total of 1765 consecutive patients with hHCC who underwent initial intra-arterial therapies were reviewed and divided into a TACE group.